What Is a Commutator in an Electric Motor?
🚗 Types of Electric Motors
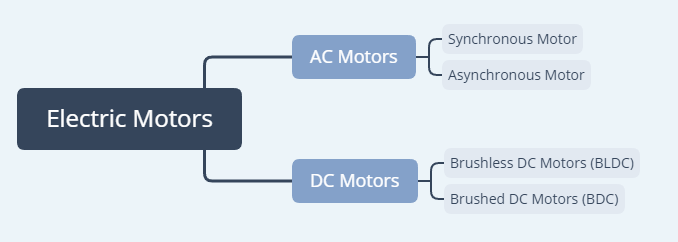
Pic. 1 Types of Electric Motors
Electric motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. There are three main types:
- DC Motors (Direct Current): Use a commutator to maintain one-way rotation by switching current direction.
- AC Motors (Alternating Current): Powered by alternating current, with no need for mechanical switching.
- Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): Rely on electronic commutation using sensors instead of mechanical commutators.
- Synchronous Motor: One of type of AC motors.
- Asynchronous Motor: One of type of AC motors.
-
Brushed DC Motors (BDC): One of type of DC motors.
👉 This article focuses on DC motors, where the commutator plays a critical role in operation.
⚙️ How Does a Commutator Work?
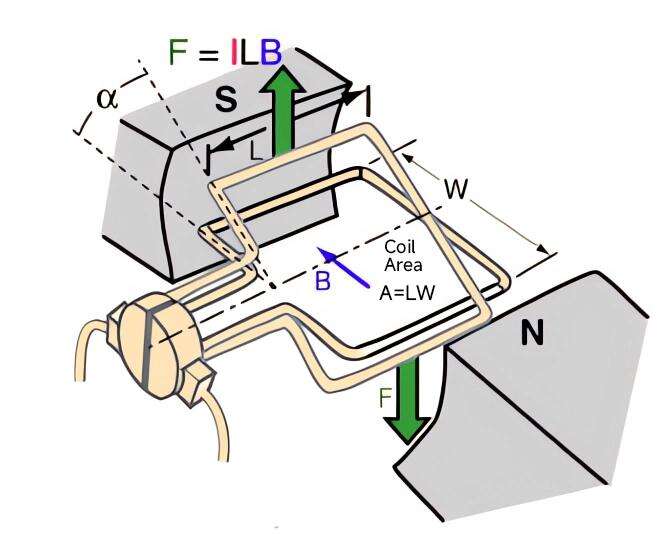
Pic. 2 Torque in a magnetic field
The lever arm for the torque produced on the armature varies with the angle of the coil (cos α). Therefore, when the coil is perpendicular (vertical) to the magnetic field of the stator, no torque is produced. This is why DC motors have multiple coils.
Image credit: Georgia State University
A commutator is a split copper ring attached to the rotor (also called the armature) of a DC motor. It works together with carbon brushes that deliver current to the rotor.
The Working Principle:
1.When current flows through a coil, a torque (twisting force) is generated in the magnetic field.
2.As the coil rotates, if the direction of the current remains unchanged, the direction of the electromagnetic force will change, causing the motor to stop or reverse.
3.The commutator automatically switches the direction of the current once every 180° of rotation, keeping the torque in the same direction.
🔄 Shortly, the commutator turns the coils on and off to control which direction the electromagnetic fields are pointing.
🔩 Core Components of a DC Motor
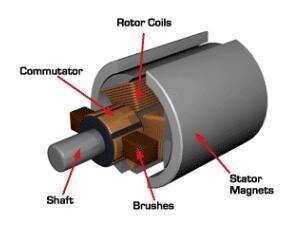
Pic. 3 Basic structure of a DC motor
Image credit: electrical4u.com
| Component | Function |
| Stator | Provides a fixed magnetic field |
| Rotor/Armature | Rotating part with windings |
| Commutator | Reverses current direction during rotation |
| Brushes | Conduct current from the power source to the commutator |
🧠 Key insight: The commutator and brushes form a contact system that ensures the electromagnetic force always points in the same direction, enabling smooth rotation.
🔌 What Does a Commutator Do?
-
💡 Keeps rotation unidirectional: Prevent the motor from stopping or reversing every 180° rotation.
-
🔁 Reverses coil current: Switches polarity at just the right moment.
- 🔥 Controls electromagnetic polarity: Ensures proper flow of electricity into and out of the armature windings.
📷 Visual tip: Think of the commutator as a timed switch that flips the current every half-rotation, maintaining continuous motion.
📈 Why Is the Commutator Important?
-
✅ Enables continuous rotation: Without it, the motor would oscillate back and forth.
-
⚙️ Maintains steady torque output: Keeps the armature force aligned with the rotation direction.
-
🧯 Prevents short-circuiting and sparking: Thanks to the “neutral zone” where induced voltage is zero.
- 🧲 Improves efficiency: Modern commutators use high-quality copper segments (and a small amount of silver) and carbon brushes for durability and low friction.
📝 Summary
The commutator is a vital part of a DC motor that switches current direction within the armature, allowing for smooth and continuous rotation.

