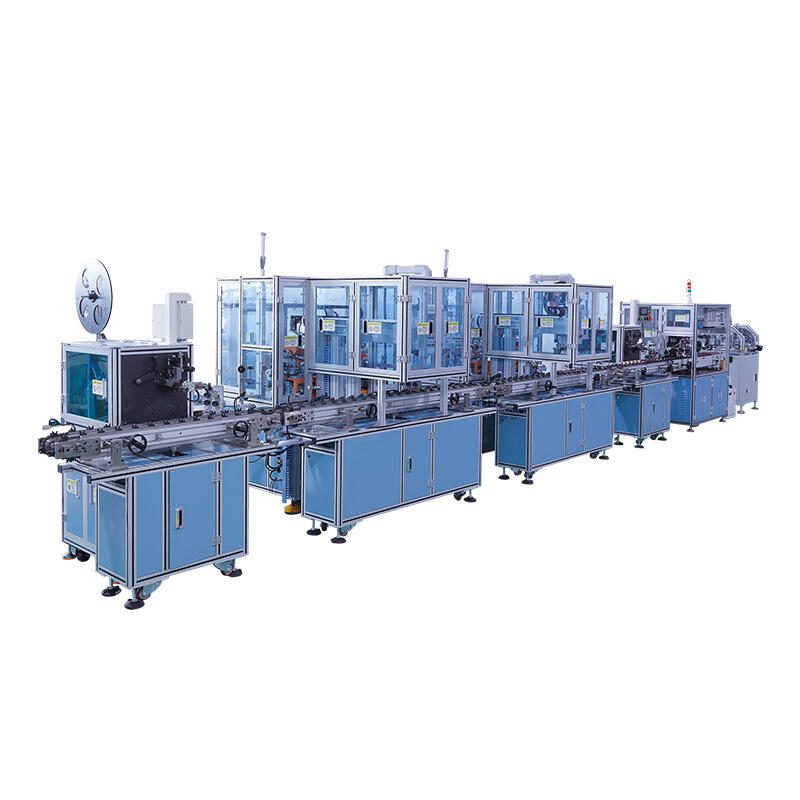
The FPV drone industry continues to experience unprecedented growth, driving manufacturers to seek efficient solutions for scaling their motor production capabilities. Building a streamlined motor production line has become essential for companies looking to meet increasing demand while maintaining quality standards and competitive pricing. Modern manufacturing approaches emphasize lean principles that eliminate waste, reduce setup times, and maximize throughput without compromising precision. The key to success lies in implementing automated systems that can adapt to various motor specifications while maintaining consistent output quality.
Understanding Modern Motor Manufacturing Requirements
Industry Standards and Quality Expectations
FPV motor manufacturing must adhere to strict tolerance requirements that directly impact drone performance and reliability. Modern motors require precise winding patterns, balanced rotor assemblies, and consistent magnetic alignment to achieve optimal efficiency ratings. The industry demands motors that can withstand high RPM operations while maintaining thermal stability under extreme conditions. Quality control systems must validate each component throughout the production process to ensure compliance with aerospace and consumer electronics standards.
Manufacturing specifications typically include rotor balance tolerances within 0.5 grams per centimeter, winding resistance variations below 2%, and magnetic field uniformity standards that affect motor smoothness. These requirements necessitate sophisticated testing equipment and automated inspection systems that can verify component quality at production speeds. Temperature cycling tests, vibration resistance evaluations, and electromagnetic compatibility assessments form essential parts of the quality validation process.
Production Volume and Scalability Considerations
Modern FPV motor demand fluctuates significantly based on seasonal trends, new product launches, and market competition dynamics. Production lines must accommodate varying batch sizes while maintaining economic efficiency across different volume scenarios. Flexible manufacturing systems allow manufacturers to switch between motor types and specifications without extensive retooling or prolonged downtime periods. The ability to scale production from prototype quantities to mass production volumes provides competitive advantages in rapidly evolving markets.
Capacity planning requires careful analysis of market forecasts, component supplier capabilities, and downstream assembly requirements. Successful motor production line implementations often incorporate modular expansion capabilities that allow manufacturers to add capacity incrementally as demand grows. This approach minimizes initial capital investment while providing pathways for future growth without disrupting existing operations.
Essential Components of Lean Motor Production
Automated Assembly Systems
Core automation components include precision winding machines that can handle multiple wire gauges and winding patterns with minimal changeover time. Advanced servo-controlled systems position rotors and stators with micron-level accuracy while maintaining consistent tension throughout the winding process. Automated insertion equipment places magnets, bearings, and housing components with repeatable precision that exceeds manual assembly capabilities. Vision-guided robots verify component orientation and detect potential defects before final assembly stages.
Integration between individual stations requires sophisticated control systems that coordinate material flow, timing sequences, and quality checkpoints. Programmable logic controllers manage station-to-station communication while tracking individual motor assemblies through their complete production cycle. Real-time monitoring systems collect performance data that enables predictive maintenance scheduling and continuous process optimization initiatives.
Quality Control and Testing Integration
Inline testing stations perform electrical, mechanical, and performance evaluations without removing motors from the production flow. Automated test equipment measures parameters including no-load current, torque constants, and speed-torque characteristics under controlled conditions. Statistical process control systems analyze test results to identify trends that might indicate tooling wear, material variations, or process drift before they affect product quality.
Advanced testing protocols include burn-in procedures that verify motor performance under accelerated aging conditions. Environmental testing chambers subject sample motors to temperature cycling, humidity exposure, and vibration stress to validate durability specifications. Data collection systems maintain comprehensive test records that support traceability requirements and enable continuous improvement initiatives based on field performance feedback.
Implementation Strategies for Rapid Deployment
Modular System Architecture
Modular production systems enable faster implementation timelines by utilizing pre-engineered components that integrate seamlessly with existing manufacturing infrastructure. Standardized interfaces between stations simplify installation procedures while reducing commissioning time and complexity. Pre-tested automation modules arrive ready for integration, minimizing on-site debugging and reducing project risk factors. This approach allows manufacturers to achieve production readiness within weeks rather than months typically required for custom-engineered solutions.
Component standardization extends to control systems, safety interlocks, and operator interfaces that maintain consistency across different production areas. Operators can transition between stations with minimal additional training, improving workforce flexibility and reducing labor costs. Maintenance personnel benefit from standardized components that simplify spare parts inventory and troubleshooting procedures.
Supplier Partnership and Integration
Strategic partnerships with equipment suppliers provide access to proven technologies and implementation expertise that accelerate project timelines. Collaborative engineering approaches combine supplier capabilities with manufacturer requirements to develop optimized solutions. Joint development programs often result in customized equipment that addresses specific production challenges while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Supplier-provided training programs ensure operators and maintenance personnel achieve proficiency quickly.
Long-term partnership agreements typically include ongoing support services, technology updates, and performance optimization consulting that maximize return on investment. Suppliers with extensive industry experience can recommend process improvements based on best practices observed across multiple implementations. This knowledge transfer accelerates the learning curve and helps manufacturers avoid common pitfalls that delay project completion.
Optimization Techniques for Maximum Efficiency
Lean Manufacturing Principles
Value stream mapping identifies opportunities to eliminate non-value-adding activities throughout the production process. Detailed analysis of material flow, operator movements, and information transfer reveals inefficiencies that increase cycle times and production costs. Single-minute exchange of die principles reduce changeover times between different motor configurations, enabling smaller batch production without economic penalties. Continuous flow manufacturing minimizes work-in-process inventory while improving cash flow and reducing storage requirements.
Error-proofing techniques prevent defects from occurring rather than detecting them after they happen. Mechanical fixtures ensure correct component orientation while sensors verify proper assembly sequence completion. Automated systems eliminate human error sources in critical operations such as torque application, adhesive dispensing, and final inspection procedures. These preventive measures reduce scrap rates and rework costs while improving overall equipment effectiveness.
Data-Driven Process Control
Real-time production monitoring systems collect comprehensive data about machine performance, quality metrics, and operator efficiency. Advanced analytics identify patterns that predict equipment failures, quality issues, and production bottlenecks before they impact output. Machine learning algorithms optimize process parameters automatically based on historical performance data and current operating conditions. This intelligent automation improves consistency while reducing the need for manual intervention.
Predictive maintenance programs utilize vibration analysis, thermal monitoring, and oil analysis to schedule maintenance activities during planned downtime periods. Condition-based maintenance strategies reduce unexpected failures while optimizing maintenance costs. Integrated maintenance management systems coordinate spare parts inventory, technician scheduling, and documentation requirements to minimize maintenance duration and maximize equipment availability.
Technology Integration and Future-Proofing
Industry 4.0 Implementation
Smart manufacturing technologies enable remote monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making that optimize production performance continuously. Internet of Things sensors collect data from individual machines and components, providing unprecedented visibility into production operations. Cloud-based analytics platforms process large datasets to identify optimization opportunities that might not be apparent through traditional monitoring methods. Digital twin technologies simulate production scenarios to evaluate process changes before implementation.
Artificial intelligence applications include quality prediction models that adjust process parameters proactively to maintain specification compliance. Machine vision systems equipped with deep learning capabilities detect subtle defects that human inspectors might miss. Automated scheduling algorithms optimize production sequences based on material availability, equipment capacity, and delivery requirements while considering energy costs and labor constraints.
Scalability and Adaptability Features
Future-ready production lines incorporate expandable architectures that accommodate new motor designs and changing market requirements. Reconfigurable automation systems allow manufacturers to modify production processes without extensive equipment replacement. Software-defined manufacturing capabilities enable rapid response to customer specification changes through parameter adjustments rather than hardware modifications. These flexibility features protect capital investments while enabling competitive responsiveness.
Standardized communication protocols ensure compatibility with future equipment additions and technology upgrades. Open architecture control systems prevent vendor lock-in situations while enabling integration of best-in-class components from multiple suppliers. This approach maximizes long-term value while minimizing technology obsolescence risks that could impact competitiveness.
Cost Optimization and Return on Investment
Capital Investment Strategies
Phased implementation approaches spread capital requirements over time while generating cash flow from initial phases to fund subsequent expansions. Lease financing options reduce upfront costs while providing access to latest technology versions. Equipment suppliers often offer flexible payment terms that align with production ramp-up schedules and revenue generation timelines. These financing strategies enable manufacturers to implement comprehensive motor production line solutions without straining cash flow or delaying market entry.
Total cost of ownership calculations must include energy consumption, maintenance requirements, operator training costs, and expected equipment lifecycle. Advanced automation typically requires higher initial investment but delivers lower operating costs through reduced labor requirements and improved efficiency. Energy-efficient systems minimize ongoing operational expenses while supporting sustainability initiatives that increasingly influence customer purchasing decisions.
Performance Metrics and Monitoring
Key performance indicators include overall equipment effectiveness, first-pass yield rates, and cycle time consistency measurements. Labor productivity metrics track operator efficiency and identify training opportunities that improve performance. Quality cost tracking quantifies the financial impact of defects, rework, and customer returns to justify quality improvement investments. These metrics provide objective data for evaluating production line performance and identifying optimization opportunities.
Regular performance reviews compare actual results against projected benefits to ensure investment objectives are achieved. Variance analysis identifies factors that impact performance and guides corrective action development. Continuous improvement programs utilize performance data to prioritize enhancement projects that deliver maximum return on investment. This systematic approach ensures production lines continue delivering value throughout their operational lifecycle.
FAQ
What is the typical implementation timeline for a new motor production line
Implementation timelines vary based on complexity and customization requirements, but most standard motor production lines can be deployed within 12-16 weeks from order placement. This includes equipment design, manufacturing, delivery, installation, and commissioning phases. Modular systems often achieve faster deployment schedules, while highly customized solutions may require additional time for engineering and testing. Proper project planning and supplier coordination are essential for meeting aggressive timeline objectives.
How can manufacturers minimize production line downtime during implementation
Phased implementation strategies allow manufacturers to maintain existing production capacity while installing new equipment incrementally. Off-line testing and commissioning procedures verify system performance before integration with production operations. Parallel production approaches enable continuous output during transition periods. Comprehensive operator training programs ensure workforce readiness when new systems become operational, minimizing learning curve disruptions.
What factors determine the optimal level of automation for motor production
Production volume requirements, quality specifications, labor costs, and available capital influence automation level decisions. High-volume operations typically justify greater automation investment through labor cost savings and improved consistency. Complex motor designs may require specialized automation to achieve required precision levels. Market volatility and product lifecycle considerations also affect automation strategies, with flexible systems preferred for dynamic markets.
How do manufacturers ensure compatibility with existing quality management systems
Modern production line control systems offer configurable data collection and reporting capabilities that integrate with existing quality management databases. Standardized communication protocols enable seamless data transfer between production equipment and enterprise systems. Customizable reporting formats ensure compliance with internal quality procedures and external certification requirements. System integration specialists can configure interfaces that maintain data integrity while minimizing operational disruptions.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Modern Motor Manufacturing Requirements
- Essential Components of Lean Motor Production
- Implementation Strategies for Rapid Deployment
- Optimization Techniques for Maximum Efficiency
- Technology Integration and Future-Proofing
- Cost Optimization and Return on Investment
-
FAQ
- What is the typical implementation timeline for a new motor production line
- How can manufacturers minimize production line downtime during implementation
- What factors determine the optimal level of automation for motor production
- How do manufacturers ensure compatibility with existing quality management systems

